3232853 - 1080B exhaust emission control system
The electronic control unit identifies the composition of the mixture (rich or lean) from the Lambda sensor output voltage.It adjusts the quantity of fuel injected to ensure the optimum composition of the mixture (l = 1) to create the ideal conditions for the treatment of the exhaust gases in the catalytic converter.If the mixture is too rich (lambda less than 1), then the quantity of fuel should be reduced and, if the mixture is too lean (lambda greater than 1), then the quantity of fuel should be increased.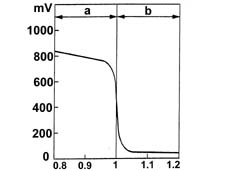
Catalytic converter
The oxidizing catalytic converter is a post-treatment device for oxidizing the CO, HC and particle matter, transforming them into carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) and water vapour (H 2 O). The catalytic converter consists of a ceramic, honeycomb structure monolith (1) with cells impregnated with platinum (2), which acts as a catalyst for the oxidation process.The exhaust gases which pass through the cells heat the catalyzer, triggering the conversion of the pollutants into inert compounds.The chemical reaction which causes the oxidation of the CO, HC, and particle matter takes place at temperatures of between 200 and 350° C.In effect, at temperatures above 350° C the sulphur, contained in the diesel fuel, starts to oxidize, producing sulphur dioxide and sulphuric anhydride.