125000352 - INTRODUCTION - ANTI-LOCK BRAKING SYSTEM (A.B.S.)
CONSTRUCTION SPECIFICATIONS
The Alfa GT is equipped with an ABS/EBD brake control system.The ABS/EBD system is the Bosch 5.7 type, developed from the 5.3 ABS system already used on other Alfa Romeo vehicles.The ABS is fitted parallel to the hydraulic braking system so that should it not work braking would still be guaranteed.The ABS incorporates the EBD function (Electronic Brake force Distribution) therefore the hydraulic system does not have a rear load proportioning valve.VIEW OF ASSEMBLY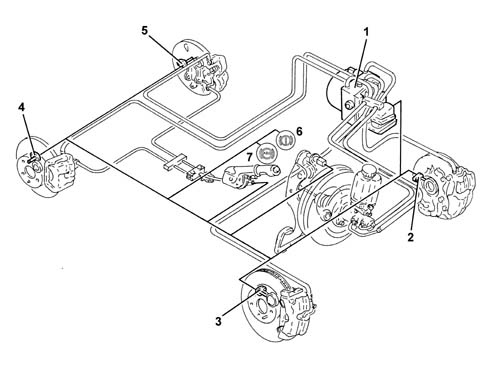
SPECIFICATIONS
The Bosch 5.7 A.B.S. control unit is a version developed from the previous 5.3 A.B.S. and is connected to the C-CAN taking the name NFR (brake node) and comes in three versions:
- ABS 5.7 with EBD
- ABS 5.7 with EBD with ASR/MSR (drive control) Characteristic of working principle 3350A ANTI - SPIN REGULATION DEVICESand VDC (vehicle dynamic control)
- Characteristic of working principle 3350E VEHICLE DIRECTION CONTROL SYSTEM VDC
| The ABS with VDC incorporates the ASR/MSR logic, the ASR system is not available by itself. |
The control unit receives and transmits information on the C-CAN and supports the following functions:
- acquiring a direct speed signal for the four wheels and processing and transmitting the signal via the C-CAN
- acquiring a direct signal for the drive wheel speed and processing and transmitting the signal via the C-CAN for the milometer
- sending the speed signal (V.S.O.) on a discreet line to the Body Computer (used if there are problems with the C-CAN.
- directly acquiring the vehicle brake lights control signal: NA only for ABS, both NA and NC for VDC
- managing the ABS, EBD and VDC warning lights via the C-CAN line and acquiring feedback on the warning light status from the NQS
- Autodiagnosis on a direct line (K line).
COMPOSITION
Structure
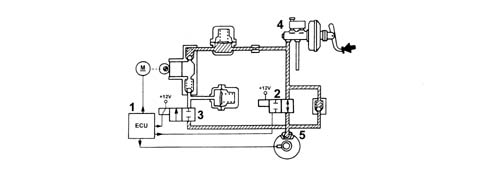
The ABS 5.7 system consists of:
- an electronic control unit integral with the hydraulic control unit
- a hydraulic control unit that modulates braking pressure by means of eight solenoids, two for each wheel
- four ACTIVE MAGNETORESISTIVE sensors that record wheel angular speed of rotation
- wiring with specific connector
OPERATION
General remarks
The electronic control unit processes signals from the active sensors and brake light control switch. It identifies the wheel or wheels with a tendency to lock (maximum slip between wheel and road surface) by means of the control unit software and modulates the brake fluid pressure selectiely for the front wheels and in tandem for the rear wheels (select-low function).The ABS modulates brake pressure in accordance with three basic stages:
- 1st pressure maintenance stage
- 2nd pressure reduction stage
- 3rd pressure increase stage.
Operating strategies
Pressure increase stage without intervention of abs
When the brake pedal is pressed, the electronic control unit (1):
- does not supply load solenoid (N.O.) (2)
- does not supply discharge solenoid (N.C.) (3)
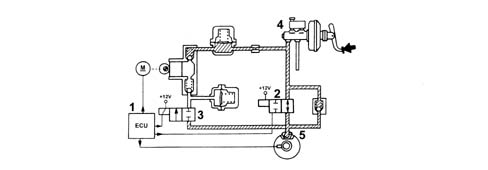
Example of abs intervention
Pressure maintenance stageControl unit (1):
- supplies load solenoid (N.O.) (2)
- does not supply discharge solenoid (N.C.).
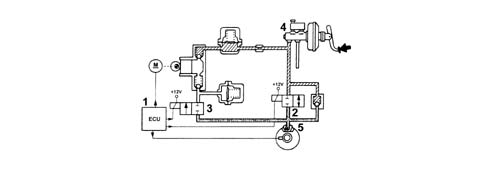
The control unit:
- supplies load solenoid (N.O.) (2)
- supplies discharge solenoid (N.C.) (3)
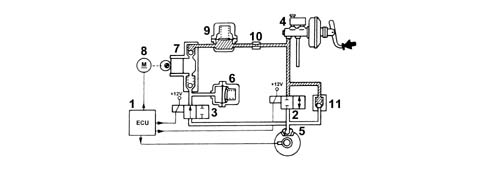
Control unit (1):
- does not supply load solenoid (N.O.) (2)
- does not supply discharge solenoid (N.C.) (3)
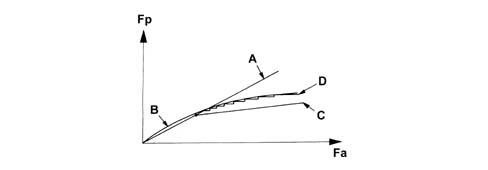
Ebd function (electronic brake-force distribution)
The EBD function controls brakeforce distribution and thus replaces the conventional mechanical load proportioning valve allowing:
- exclusive action on the rear brake calipers
- improved brakeforce distribution
- optimal intervention under all load conditions (static or dynamic), driving conditions (straight line or corners) or car condition (tyres, brakes and suspension worn)
- implementation of a strategy that follows the ideal distribution curve.
EBD function failure is indicated by simultaneous activation of:
- ABS warning light
- low brake flud and/or handbrake on warning light.
Recovery
The electronic control unit comes with a safety circuit that supervises ABS efficiency.With key on, the safety circuit carries out an initial autotest for 4 seconds to check:
- electronic control unit operation
- solenoid activation to check operation
- the C-CAN network
When the car is in motion, the safety circuit works as follows:
- continually compares angular wheel speed with the calculated reference speed
- checks memory condition
- checks operation of both relays, the solenoids and the pump motor
- continually checks battery voltage
- checks brake pedal switch efficiency
- checks C-CAN network efficiency
If the safety circuit detects one or more faults in system components during the check stage, the safety circuit operates as follows:
- deactivates the ABS while still guaranteeing operation of the conventional braking system
- indicates the fault status to the driver by turning on a warning light on the control panel.