244000371 - ASSEMBLY INDEX
GLOSSARY
Hardened and tempered steel
Special steel that has undergone a hardening and tempering treatment.Heata treatment applied to special steels to improve their mechanical properties: it involves hardening followed by tempering to make the material much stronger.Tempering: consists of heating at temperatures %lt; 720°C followed by slow cooling in order to lessen the effects of the tempering without removing them. In this way, the material returns to conditions that are closer to a stable chemical and physical balance.Hardening: this is achieved when the metal structure is at a high temperature when it is harder and more resistant than when cold.
Condensation
This is the change of a substance from a vapour to a liquid state, the opposite of evaporation; it takes place through compression or cooling.
Denotation
This is abnormal combustion of the mixture that takes place extremely rapidly.It is detected by metallic noises in the cylinder head and a gradual reduction in power.The phenomenon is basically linked to the engine compression ratio and the specifications of the fuel that makes up the mixture.
CONSTRUCTION SPECIFICATIONS
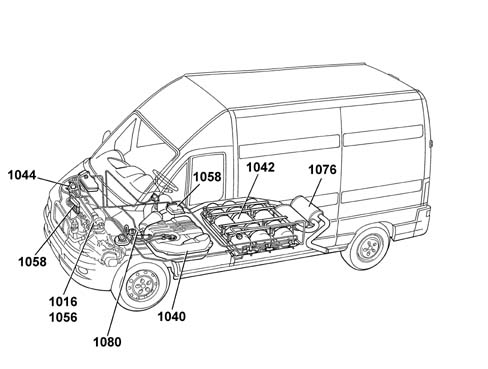
4 cylinder in line, 8 valve 1998 cc engine with SOHC and Magneti Marelli IAW 48P2 electronic injection/ignition system.The unit is a system made up of the engine and all circuits required for its operation:fuel feed circuitmethane supply systemair intake circuitexhaust system with catalytic converterfuel vapour recirculation systemengine cooling systemengine lubrication systemThe Fiat Ducato bipower features two fuel supply systems so that it can run either on conventional "petrol" or or "compressed natural gas" fuel (CNG).The system for running on two types of fuel comprises the basic Magneti Marelli IAW 48P2 system for petrol operation and the Metatron METAFUEL 5D0 system for operating on methane.The two systems are connected via a high speed CAN line.The METAFUEL system is clear for the basic system for all components and the operation of the basic system is not affected in all operating conditions.The two control units share some of the system elements. The division is clear for the basic system (for further details see.Characteristic of working principle1056ALIMENTAZIONE INIEZIONE BENZINA(Vedere sottogruppo ) 1058 The natural gas consists mainly of methane but contains small quantities of other hydrocarbons and inert gases in percentages that vary according to the origins of the CNG. For this reason natural gas is usually known as methane and will be referred to that from now onwards.The transformation of the engine consists of the addition of components in the methane fuel supply system, in other words the canisters, a special manifold, special injectors, the methane fuel system management electrical system and valve seats made from a low wear material.The system features the injection of the methane fuel into the individual inlet manifolds, thereby creating a Phased Sequential Multipoint injection system similar to the one for traditional petrol systems (which remains unaltered).The advantage of this solution is that the driveability and performance of the vehicle are not altered in any way whatsoever when the engine is running on petrol (for systems available commercially through conversion kits, a Venturi pipe is introduced into the engine intake manifold). Running on methane gives a performance that is totally in line with running on petrol, something that was not previously the case in vehicles that were converted, with only a slight reduction as a result of the decrease in maximum power and torque compared with petrol operation due to the decreased cylinder refilling.Whilst the engine is running on methane there is always the improvement in terms of the reduction in pollutant exhaust emissions.This improvement is particularly significant in terms of unburnt hydrocarbons. These basically consist of methane whilst the quantities of more complex molecule hydrocarbons are negligible. This difference is very important: methane is not harmful because as its molecules are stable they are not very reactive. It does not therefore give rise to damaging and tiresome photochemical smog and does not contribute to the formation of ozone which, being a powerful oxidizing agent, damages organic matter.
Fuel supply system
Two different fuel supply systems are present.The (conventional) petrol system with a fuel pump submerged in the tank and enclosed in a container together with the level gauge and filter; the fuel pressure regulator on the air intake manifold.The methane system includes a series of canisters, connected in paralle, a pressure reduction unit and special injectors located on the intake manifold.Characteristic of working principle1040SERBATOIO COMBUSTIBILE E TUBAZIONI(Vedere sottogruppo ) 1042 Characteristic of working principle1044POMPA/E E DISPOSITIVI DEL CIRCUITO DI ALIMENTAZIONE
Air supply system
Air supply system with an intake manifold made out of synthetic material that doubles as a fuel manifold and large air filter housing to limit intake noise.
Exhaust system
The exhaust system is fitted with a three-way catalytic converter and two Lambda sensors, one downstream and one upstream of the catalytic converter, (for further details see.Characteristic of working principle1076TUBAZIONI DI SCARICO E SILENZIATORI(Vedere sottogruppo ) 1080
Emission control system
The following emission control systems are used on this model:Exhaust emission control system with a three-way catalytic converter and two Lambda sensors, one downstream and one upstream of the catalytic converter;crankcase vapour/gas recirculation system;fuel evaporation control system; for further details
COOLING SYSTEM
Forced circulation with centrifugal vane pump for further detailsCharacteristic of working principle1088RAFFREDDAMENTO MOTORE
GLOSSARY
Aramidic
Special type of asbestos-free fibre used to make cylinder-head gaskets.
LPG
LPG (Liquid Petroleum Gas) is a mixture of hydrocarbons (propane, butane, isobutane, propylene etc.) that are in a gasous state at atmospheric pressure.At normal environmental temperature, the mixture can be liquified at a relatively low pressure (8 bar).
Calorific power
Represents the energy content of a fuel.This alters in relation to the amount of carbon and hydrogen present in the fuel. The higher the hydrogen/carbon ratio, the higher the calorific potential.It is obvious that, all else being equal, a higher calorific potential corresponds to a lower fuel consumption.
Evaporation
This occurs when a substance changes from a liquid state to a gaseous state. It occurs due to expansion or heating of the substance.
Endothermic
Particular type of chemical reaction that involves absorption of heat from the surrounding environment and a consequent temperature drop.When a liquid gas expands, an endothermic reaction takes place. The temperature of items in contact with the expanding gas can drop to -40 °C in the gas of LPG.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
 | LPG systems may be serviced only by staff who have attended one of the LPG training courses organised by individual markets. Authorised staff must comply with current legal regulations and take care to observe all safety requirements learnt during the training course. The standards listed below must be observed during any operation carried out on a vehicle equipped with an LPG system. |
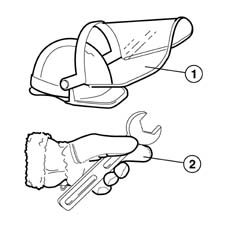
Although Liquid Petroleum Gas (LPG) fuel systems are no more dangerous in practice than normal petrol systems, they need special attention, particularly with regard to servicing.In particular, when opening connectors or moving pressurised components, operators must be equipped with helmets with face visors (1) to UNI-EN 166 standards to protect against spray and winter gloves (2) to UNI-EN 388 and UNI-EN 511 standards to protect their hands against frostbite due to the heat absorbed by the expanding LPG.
The system used on the Fiat Ducato meets requirements in the individual countries where it is marketed.One-way valves are fitted to the tank at the inlets for the LPG pipes from the filler fitting and the return pipe from the injector. These prevent gas accidentally emerging from the tank.Solenoids located: one near the outlet pipe on the tank flange and one on the outlet pipe in the engine bay, insulate both outlet pipe sections when petrol fuel mode is selected or the engine is off.A third solenoid is located on the return pipe to insulate the pipes from the tank if the vehicle crashes and the inertia switch cuts in.The one-way valve on the filler fitting prevents the LPG in the filler pipe from returning to the outside.Despite the presence of these devices, it must be remembered that LPG is still a gas under environmental conditions and thus can easily explode. Always observe the following warnings when leaks are potentially present and during any service operations on the system.do not smoke.do not use naked flames.do not use driers and power tools.do not use incandescence lamps.do not wear acrylic clothing that generates static electricity.always disconnect the battery terminals.when the vehicle is in the workshop, do not park near inspection pits, intake port drainage wells or any closed area without sufficient ventilation. Danger of explosion: LPG is heavier than air and tends to sink to the lowest possible level. It will therefore fill any openings near the vehice to create dangerous, potentially explosive gas pockets.do not use the following workshop equipment: air compressors, current generators, suction devices, power tools etc. that could generate sparks and thus trigger explosions in the case of leaks.do not use any type of suction device; always work in ventilated areas.do not take vehicles with LPG systems into closed environments if they been in an accident or if the condition of the system seals is unknown.if the vehicle is placed in a drying oven after painting at a temperature greater than 80°C, remove the LPG tank from the vehicle.because different material types are used to make the LPG system, potential differences may arise that generate electrostatic charges. For this reason, discharge any electrostatic charges as follows before working on each system component.disconnect the battery negative terminal and positive terminal;join both battery terminals by means of an earth lead. This will discharge any electrostatic charges that may have built up.
CONSTRUCTION SPECIFICATIONS
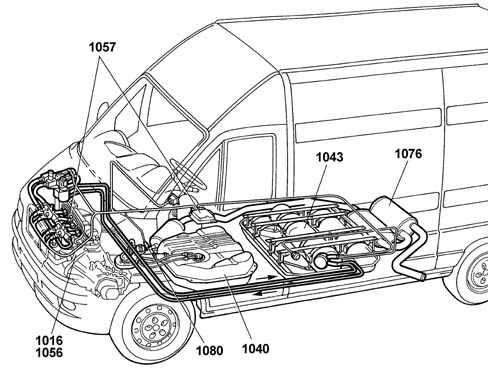
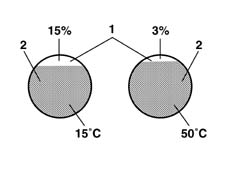
4 cylinder in-line engine, 8 valves, 1998 c.c., one overhead camshaft, with Magneti Marelli IAW 48P.2 electronic injection - ignition system.The unit is a system made up of the engine and all circuits required for its operation:fuel supply system.LPG supply systemair intake circuitexhaust system with catalytic converterfuel vapour recirculation systemengine cooling systemengine lubrication systemThe Fiat Ducato comes with two fuel systems so it is able to run equally well on conventional petrol or Li quid Petroleum Gas (LPG).The dual fuel system comprises the basic petrol system (Magneti Marelli IAW 48P2) and an integral system for LPG operation.The two systems are connected via a high speed CAN line.All components of the LPG are transparent to the basic system and the operation of the basic system is not affected under any operating conditions.The two control units share some of the system elements. This sharing is transparent to the basic system.(Vedere sottogruppo ) 1057 Liquid Petroleum Gas (LPG) consists mainly of two hydrocarbons, propane and butane.LPG is obtained mainly from:oil refinery processesdegassing of natural gas (separation of liquid hydrocarbons present in natural gas).Like all petroleum gases, LPG is heavier than air, colourless and odourless. A scented additive (Merceptane) is added so that its presence can easily be detected.Due to its composition, LPG can easily be converted from its natural gaseous state (15°C) to a liquid state by applying a slight pressure increase (7.5 bar).Due to these properties, the gaseous part (1) and the liquid part (2) are in a state of equilibrium in the tank.Whenever LPG is drawn off, part of the liquid evaporates to re-establish the equilibrium between liquid and gas.Because the volume of liquid LPG increases by 0.25% for each degree centigrade temperature increase, it is essential to ensure that the tank is filled to only 80% of its capacity at most to allow the liquid to expand as the temperature increases (environment, vehicle operation).
LPG has been used in automotive engines since the Fifties. It is popular due its excellent antiknock properties and the fact that combustion takes place without the formation of residues in the combustion chamber.Because they do not contain aromatic compounds or additives such as sulphur and lead, emissions produced by LPG combustion are significantly less polluting than petrol engine emissions.An engine can be converted to run on LPG by changing the material used for the valve seats and adding the parts included in the LPG system, i.e. cylinder, inlet and recirculation pipes, special injectors and an LPG system electronic management unit.The valve seats must be made out of material that is very resistant to wear and heat because, unlike petrol, LPG is a very poor lubricant.LPG in the liquid state is injected into the individual intake ports to create a Phased Sequential Multipoint system similar to those used with conventional petrol fuel systems (unaltered).This new LPG injection system has been adopted due to a need to make the use of LPG more economical and also improve performance and emission control.In the past, the best conventional LPG systems (with evaporator and mixer) could compete on equal terms with petrol systems from the viewpoint of cost and emissions, but suffered the disadvantages of flashback and response lag.Technological developments led to the introduction of systems that firstly injected gas in the gaseous phase and now in the liquid phase as normally occurs with petrol.The gaseous phase injection system was the first development of the conventional systems with evaporator and mixer. The difficulty with these systems was to find gaseous fluid injectors that could offer a level of accuracy comparable to that of liquid injectors.In this type of system, fuel is metered by a step motor that modulates LPG output according to fuel requirements. The gas is introduced downstream of the throttle body by means of mechanical diaphragm injectors operated by the vacuum in the intake manifold.The introduction of the liquid phase injection system overcame these problems. Now the system could be simplified because the mixer and evaporator were no longer required while the injection could be managed in line with the petrol injection to retain the original engine strategy (idle speed control, cut-off during over-run and enrichment during acceleration and under full load), even though a special control unit was added.
Fuel supply system
Two different fuel supply systems are present.A petrol system (conventional) with fuel pump submerged in the tank and enclosed in a cradle with the level gauge and filter, fuel pressure regulator on the air intake manifold.The LPG system includes a cylindrical tank, three LPG cut-off solenoids and special injectors fitted onto a special manifold and connected via special pipes to each individual intake port.Characteristic of working principle1040SERBATOIO COMBUSTIBILE E TUBAZIONI(Vedere sottogruppo ) 1043
Air supply system
Air supply system with an intake manifold made out of synthetic material that doubles as a fuel manifold and large air filter housing to limit intake noise.
Exhaust system
The exhaust system is equipped with a trivalent catalytic converter and two lambda sensors, one downstream and one upstream of the catalytic converter.Characteristic of working principle1076TUBAZIONI DI SCARICO E SILENZIATORI(Vedere sottogruppo ) 1080
Emission control system
The following emission control systems are used on this model:Exhaust emission control system with a trivalent catalytic converter and two lambda sensors, one downstream and one upstream of the catalytic converter;crankcase vapour/gas recirculation system;fuel evaporation control system, Characteristic of working principle1080SISTEMA DI CONTROLLO EMISSIONI
GLOSSARY
Hardened and tempered steel
Special steel that has undergone a hardening and tempering treatment.Heata treatment applied to special steels to improve their mechanical properties: it involves hardening followed by tempering to make the material much stronger.Tempering: consists of heating at temperatures %lt; 720°C followed by slow cooling in order to lessen the effects of the tempering without removing them. In this way, the material returns to conditions that are closer to a stable chemical and physical balance.Hardening: this is achieved when the metal structure is at a high temperature when it is harder and more resistant than when cold.
Condensation
This is the change of a substance from a vapour to a liquid state, the opposite of evaporation; it takes place through comprssion or cooling.
Denotation
This is abnormal combustion of the mixture that takes place extremely rapidly.It is detected by metallic noises in the cylinder head and a gradual reduction in power.The phenomenon is basically linked to the engine compression ratio and the specifications of the fuel that makes up the mixture.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
 | The Ducato bipower is equipped with a high pressure methane system, designed to operate at 200 bar. It is dangerous to force the system to run at higher pressures. Do not modify either the methane system configuration or components; they have been designed exclusively for the Ducato bipower. The use of other components or materials could cause malfunctions and prejudice safety. if the vehicle is placed in a drying oven after painting at a temperature greater than 80 °C, the methane canisters must be removed from the vehicle. Although the methane system is equipped with numerous safety features, it is advisable to shut the manual tap on each canister every time the vehicle is not used for a long period, transported by other means or moved in emergencies as a result of a breakdown or accident. |
CONSTRUCTION SPECIFICATIONS
4 cylinder in line, 8 valve 1998 cc engine with SOHC and Magneti Marelli IAW 48P2 electronic injection/ignition system.The unit is a system made up of the engine and all circuits required for its operation:fuel feed circuitmethane supply systemair intake circuitexhaust system with catalytic converterfuel vapour recirculation systemengine cooling systemengine lubrication systemThe Fiat Ducato bipower features two fuel supply systems so that it can run either on conventional "petrol" or or "compressed natural gas" fuel (CNG).The system for running on two types of fuel comprises the basic Magneti Marelli IAW 48P2 system for petrol operation and the Metatron METAFUEL 5D0 system for operating on methane.The two systems are connected via a high speed CAN line.The METAFUEL system is clear for the basic system for all components and the operation of the basic system is not affected in all operating conditions.The two control units share some of the system elements. The division is clear for the basic system (for further details see "Description and operation - Subassemblies 1056 and 1058").The natural gas consists mainly of methane but contains small quantities of other hydrocarbons and inert gases in percentages that vary according to the origins of the CNG. For this reason natural gas is usually known as methane and will be referred to that from now onwards.The transformation of the engine consists of the addition of components in the methane fuel supply system, in other words the canisters, a special manifold, special injectors, the methane fuel system management electrical system and valve seats made from a low wear material.The system features the injection of the methane fuel into the individual inlet manifolds, thereby creating a Phased Sequential Multipoint injection system similar to the one for traditional petrol systems (which remains unaltered).The advantage of this solution is that the driveability and performance of the vehicle are not altered in any way whatsoever when the engine is running on petrol (for systems available commercially through conversion kits, a Venturi pipe is introduced into the engine intake manifold). Running on methane gives a performance that is totally in line with running on petrol, something that was not previously the case in vehicles that were converted, with only a slight reduction as a result of the decrease in maximum power and torque compared with petrol operation due to the decreased cylinder refilling.Whilst the engine is running on methane there is always the improvement in terms of the reduction in pollutant exhaust emissions.This improvement is particularly significant in terms of unburnt hydrocarbons. These basically consist of methane whilst the quantities of more complex molecule hydrocarbons are negligible. This difference is very important: methane is not harmful because as its molecules are stable they are not very reactive. It does not therefore give rise to damaging and tiresome photochemical smog and does not contribute to the formation of ozone which, being a powerful oxidizing agent, damages organic matter.
Fuel supply system
Two different fuel supply systems are present.The (conventional) petrol system with a fuel pump submerged in the tank and enclosed in a container together with the level gauge and filter; the fuel pressure regulator on the air intake manifold.The methane system includes a series of canisters connected in parallel, a pressure reduction unit and specific injectors located on the intake manifold (for further details see "Description and operation - Subassemblies 1040, 1042 and 1044").
Air supply system
Air supply system with an intake manifold made out of synthetic material that doubles as a fuel manifold and large air filter housing to limit intake noise.
Exhaust system
The exhaust system is fitted with a three-way catalytic converter and two Lambda sensors, one downstream and one upstream of the catalytic converter, (for further details see "Description and operation - Subassemblies 1076 and 1080").
Emission control system
The following emission control systems are used on this model:Exhaust emission control system with a three-way catalytic converter and two Lambda sensors, one downstream and one upstream of the catalytic converter;crankcase vapour/gas recirculation system;fuel evaporation control system; for further details
COOLING SYSTEM
Forced circulation with centrifugal vane pump.