312000273 - INTRODUCTION - ENGINE
GLOSSARY
Hardened and tempered steel
Heat treatment applied to special steels to improve their mechanical properties: involves hardening followed by tempering to make the material much stronger.Tempering: consists of heating at temperatures < 720°C followed by slow cooling in order to lessen the effects of the tempering without removing them.In this way, the material returns to conditions that are closer to a stable chemical and physical balance.Hardening: this is achieved when the metal structure is at a high temperature, when it is harder and more resistant than when cold.CONTROL AREA NETWORK (CAN)
The CAN is a communication network that allows the transmission of data between the ECU and other vehicle system computers.The advantage of this system lies in the fact that the need for long wiring is contained and the number of sensors reduced (because, from the moment the computers are connected by the data transmission system, the information supplied by a sensor can be used simultaneously by various devices).The CAN also allows improvement in the fault diagnosis system capacities, faster transmission of signals and electrical/magnetic compatibility of components (relationship between various electrical and electronic circuits on the vehicle and interaction between the vehicle and surrounding conditions).The circuit that connects the ECU with the other terminals is an integrated circuit known as a CAN interface. It has the function of converting the messages received via the data transmission system into the appropriate format.Condensation
This is the change of a substance from a vapour to a liquid state, the opposite of evaporation; it takes place through compression or cooling.DUCTILE CAST IRON
Ductile cast iron is cast iron that, through the addition of cerium and magnesium, contains globules or balls of carbon in a graphite state in a predominantly ferrous matrix with the consequent improvement of all mechanical and technological properties. It can therefore be forged, welded and worked with tools.It is used very extensively also because, unlike normal cast iron, it has high resistance and percentage extension values.Evaporation
The phenomenon, also known as vaporisation, when a body changes from a liquid state to a gaseous state,occurs at any temperature but, everything else being equal, the lower the temperature, the slower the change.PWM MODULATION OPERATING CYCLE
This is an impulse frequency and modulated width fixed voltage produced by the ECU for the operation of the solenoids. A PWM voltage supply consists of a series of single polarity square waves whose duration is altered by the ECU in response to demand.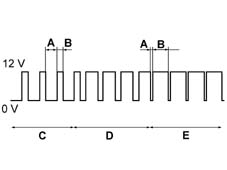
Sensor
It is a system that reacts when subject to any form of energy by changing its state, i.e. one or more of its properties (resistance, volume, temperature etc.).For example, a sensor is a material which undergoes conductivity changes when submerged in a magnetic field.New-generation sensors are solid-state devices produced using microelectronic processes that can take environmental readings and produce responses in the form of electrical signals for subsequent processing and so that final checks can be conducted.Sensors are therefore able to measure force, acceleration, pressure and temperature of gases, liquids and solids, concentration of gases such as nitrogen oxides, oxygen, etc.Viscosity
Material property whereby the particles in a body encounter resistance as they slide over one another.The resistance value or internal friction depends on the nature of the body: large in solids, very small in viscous liquids, nil in gases.In liquids, viscosity drops rapidly as temperature rises.SPECIFICATIONS
4 cylinder in line, 16 valve 1368 cc engine with TOHC with a Bosch ME 7.9.10 electronic injection/ignition system.POWER - 74 kW -100 bhp EEC at 6000 rpmTORQUE - 13.1 daNm - 13.2 kgm EEC at 4250 rpmCYLINDER ARRANGEMENT - 4 in lineBORE - 72 mmSTROKE - 84 mmCYLINDER CAPACITY - 1368 ccCYLINDER HEAD - aluminiumCRANKCASE - cast ironCRANKSHAFT - ductile cast iron with 8 counter-weights and 5 main bearings with torsional damperTIMING SYSTEM - two overhead camshafts, with drive transmission through gears with clearance recovery by intake and exhaust shafts, hydraulic tappets, 4 valves per cylinderFUEL SYSTEM - returnless system with phased sequential Bosch injectionIGNITION - completely electronic with individual coils (pencil coils)POLLUTION-CONTROL DEVICES - three-way catalytic converterLUBRICATION - forced with lobe geared pumpCOOLING - liquid with forced circulation via centrifugal pump and sealed circuit; radiator and supplementary expansion tankCOMPOSITION
The systems involved in the operation of the engine are:
- fuel supply system
- air supply system
- exhaust system with catalytic converter
- fuel vapour recirculation system
- engine cooling system.
Assembly view
.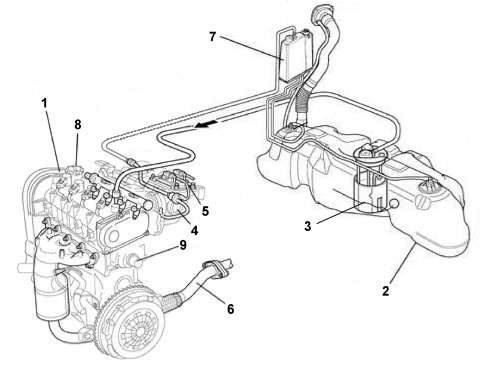
Fuel supply system
This is returnless with an electric fuel pump submerged in the tank and enclosed in a container together with the pressure regulator, the level gauge and the filter. See descriptions 1040 FUEL TANK AND PIPESAir supply system
Air supply system with plastic intake manifold and large air filter casing to limit intake noise. See descriptions 1048 ENGINE AIR SUPPLY CIRCUITExhaust system
The exhaust system has a post-treatment system for the exhaust gases with a Lambda sensor and catalytic converter fitted in the engine compartment See descriptions 1076 EXHAUST PIPES AND SILENCERSEmission control system
The following emission control systems are used on this model:
- Exhaust emission control system with a three-way catalytic converter and two lambda sensors, one downstream and one upstream of the catalytic converter;
- crankcase vapour/gas recirculation system;
- fuel evaporation control system.